24 Sep Ultrasound vs Infrared: The right tool for the job
COMPARISON OF ULTRASOUND CAMERAS AND OGI CAMERAS
Ultrasound vs Infrared: The right tool for the job
COMPARISON OF ULTRASOUND CAMERAS AND OGI CAMERAS
Ultrasound vs Infrared: The right tool for the job
Optical Gas Imaging (OGI) cameras have drastically changed the way methane and volatile organic compounds (VOC) leak detection is performed. Instead of going to each potential leak point with the so-called “sniffers” or soap spray, OGI operators are able to detect leaks meters away, speeding-up the detection and enabling to detect leaks at unexpected locations. OGI also enables to visualize gas plumes and provide valuable insights when a large release happens.
Acoustic Leak Imaging (ALI) cameras, more recently introduced, allows to detect leaks from a distance too. More affordable than OGI, they also work with any kind of gas as long as it is pressurized, and detect the leak location and not the gas plume. But each techniques has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on the application.
Through real use cases, we provide insights on:
• How these two techniques compare
• Which one suits better specific applications

Optical Gas Imaging (OGI) cameras have drastically changed the way methane and volatile organic compounds (VOC) leak detection is performed. Instead of going to each potential leak point with the so-called “sniffers” or soap spray, OGI operators are able to detect leaks meters away, speeding-up the detection and enabling to detect leaks at unexpected locations. OGI also enables to visualize gas plumes and provide valuable insights when a large release happens.
Acoustic Leak Imaging (ALI) cameras, more recently introduced, allows to detect leaks from a distance too. More affordable than OGI, they also work with any kind of gas as long as it is pressurized, and detect the leak location and not the gas plume. But each techniques has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on the application.
Through real use cases, we provide insights on:
• How these two techniques compare
• Which one suits better specific applications

Working principle
Acoustic Leak Imaging (ALI)
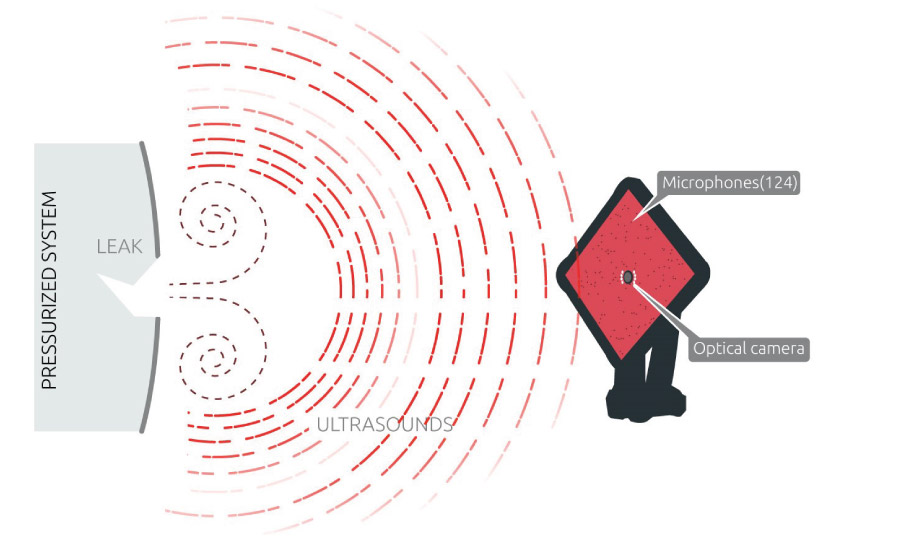
Gas leaks emit ultrasounds due to the turbulences created by the gas flow escaping a pressurized system. An ultrasound camera detects these ultrasounds using an array of microphone sensors: when a sound wave generated by a leak reaches the ultrasound camera, the sound wave hits each individual microphone at different times.
From these small-time differences, the ultrasound camera reconstructs the position of the leak source. This acoustic image is overlaid in real-time with an optical image obtained by the optical camera, allowing the user to clearly see the leak location.
Optical Gas Imaging (OGI)
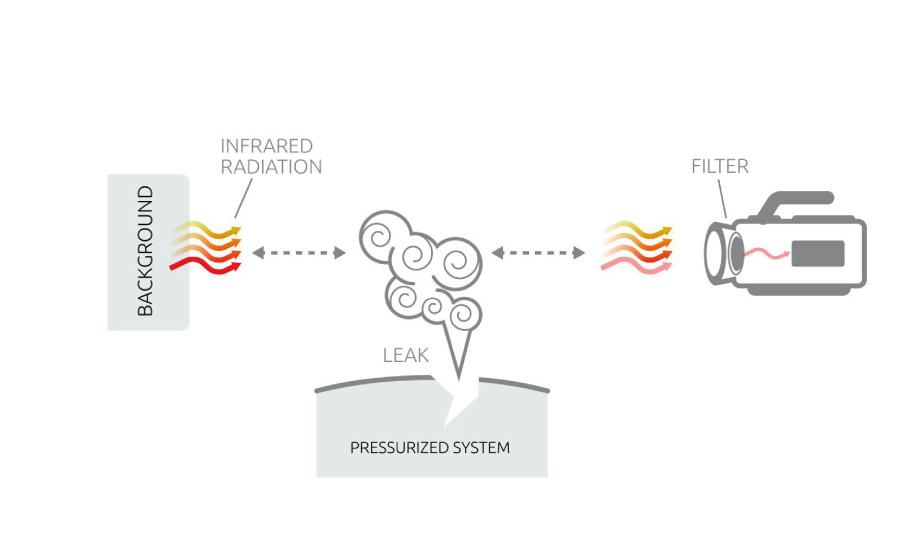
OGI cameras are a special and more sensitive type of thermal cameras, which allow the visualization of gas plumes based on the infrared absorbing nature of certain molecules. Operators can see gas plumes as a contrast between the plume and the background.
Unlike thermal cameras, OGI cameras have a filter that only transmits radiation in a specific band of the infrared region. Therefore, only gases that absorb in that specific infrared band can be detected with this filter.
Filters for detecting different gases exist, the most common application of OGI cameras being the detection of hydrocarbon leaks.
Working principle
Acoustic Leak Imaging (ALI)
Gas leaks emit ultrasounds due to the turbulences created by the gas flow escaping a pressurized system. An ultrasound camera detects these ultrasounds using an array of microphone sensors: when a sound wave generated by a leak reaches the ultrasound camera, the sound wave hits each individual microphone at different times.
From these small-time differences, the ultrasound camera reconstructs the position of the leak source. This acoustic image is overlaid in real-time with an optical image obtained by the optical camera, allowing the user to clearly see the leak location.
Optical Gas Imaging (OGI)
OGI cameras are a special and more sensitive type of thermal cameras, which allow the visualization of gas plumes based on the infrared absorbing nature of certain molecules. Operators can see gas plumes as a contrast between the plume and the background.
Unlike thermal cameras, OGI cameras have a filter that only transmits radiation in a specific band of the infrared region. Therefore, only gases that absorb in that specific infrared band can be detected with this filter.
Filters for detecting different gases exist, the most common application of OGI cameras being the detection of hydrocarbon leaks.


Working principle
Acoustic Leak Imaging (ALI)
Gas leaks emit ultrasounds due to the turbulences created by the gas flow escaping a pressurized system. An ultrasound camera detects these ultrasounds using an array of microphone sensors: when a sound wave generated by a leak reaches the ultrasound camera, the sound wave hits each individual microphone at different times.
From these small-time differences, the ultrasound camera reconstructs the position of the leak source. This acoustic image is overlaid in real-time with an optical image obtained by the optical camera, allowing the user to clearly see the leak location.

Optical Gas Imaging (OGI)
OGI cameras are a special and more sensitive type of thermal cameras, which allow the visualization of gas plumes based on the infrared absorbing nature of certain molecules. Operators can see gas plumes as a contrast between the plume and the background.
Unlike thermal cameras, OGI cameras have a filter that only transmits radiation in a specific band of the infrared region. Therefore, only gases that absorb in that specific infrared band can be detected with this filter.
Filters for detecting different gases exist, the most common application of OGI cameras being the detection of hydrocarbon leaks.

Four leaks – Two detection techniques
1. Methane leak on a connector – Refinery
This video shows how a methane leak on a connector is detected by both techniques. While the fundamental principle of the two cameras is different, both are able to detect the leak from a distance, a strong advantage over other techniques.
Nevertheless, images from ultrasound cameras have a better definition. They allow even untrained people to clearly see the exact leak location and allow for better documentation than pictures from OGI cameras.
Same leaks detected by both techniques
1. Methane leak on a connector – Refinery
This video shows how a methane leak on a connector is detected by both techniques. While the fundamental principle of the two cameras is different, both are able to detect the leak from a distance, a strong advantage over other techniques.
Nevertheless, images from ultrasound cameras have a better definition. They allow even untrained people to clearly see the exact leak location and allow for better documentation than pictures from OGI cameras.
Same leaks detected by both techniques
1. Methane leak on a connector – Refinery
This video shows how a methane leak on a connector is detected by both techniques. While the fundamental principle of the two cameras is different, both are able to detect the leak from a distance, a strong advantage over other techniques.
Nevertheless, images from ultrasound cameras have a better definition. They allow even untrained people to clearly see the exact leak location and allow for better documentation than pictures from OGI cameras.
2. Methane leak at a bolt – Detection & Quantification
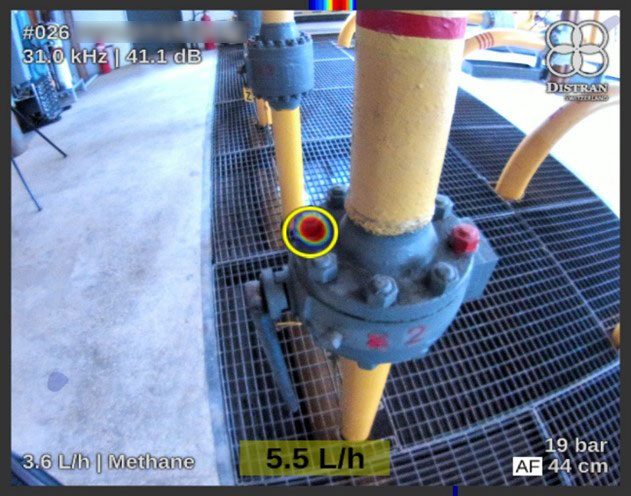

- Quantification by the ultrasound camera is immediate: the user just needs to specify the type of gas, and the system pressure.
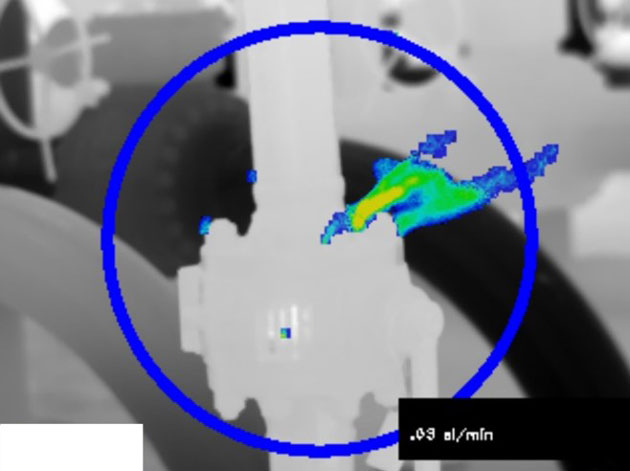
- Leak rate estimation by the OGI camera requires a tripod, few minutes, and hardware to post-process the image on the field.
2. Methane leak at a bolt – Detection & Quantification

- Quantification by the ultrasound camera is immediate: the user just needs to specify the type of gas, and the system pressure.

- Leak rate estimation by the OGI camera requires a tripod, few minutes, and hardware to post-process the image on the field.
2. Methane leak at a bolt – Detection & Quantification

- Quantification by the ultrasound camera is immediate: the user just needs to specify the type of gas, and the system pressure.

- Leak rate estimation by the OGI camera requires a tripod, few minutes, and hardware to post-process the image on the field.
3. Methane leak on a flange – Natural gas metering station
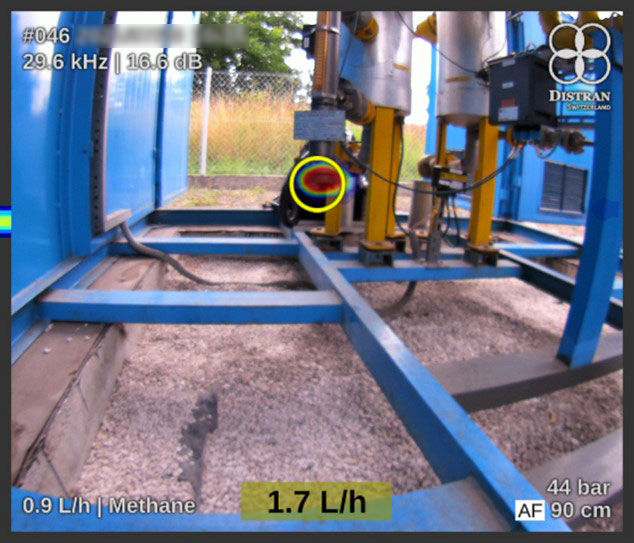

- The ultrasound camera offers a sharp visualization of the leak. This image is straightforward to interpret, showing the leak location at a 90 cm distance. By approaching the leak, the operator can even see the exact position of the leak source.
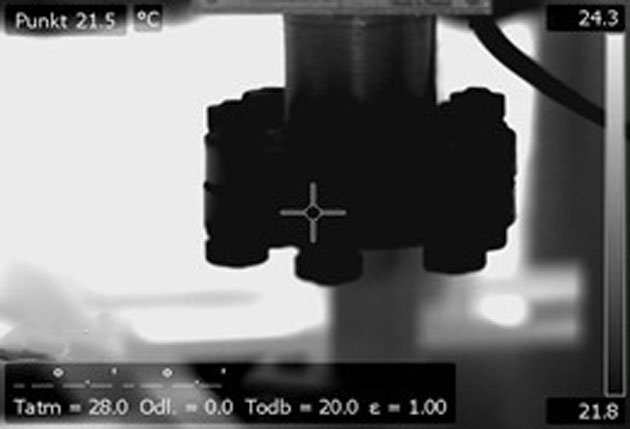
- Seen by an OGI camera: a gas plume on the lower part of the flange, where a slightly higher contrast is observed. An expert operator with an experienced eye is needed in such cases to find the right angle to detect the leak and then to interpret the images1.
3. Methane leak on a flange – Natural gas metering station

- The ultrasound camera offers a sharp visualization of the leak. This image is straightforward to interpret, showing the leak location at a 90 cm distance. By approaching the leak, the operator can even see the exact position of the leak source.

- Seen by an OGI camera: a gas plume on the lower part of the flange, where a slightly higher contrast is observed. An expert operator with an experienced eye is needed in such cases to find the right angle to detect the leak and then to interpret the images1.
3. Methane leak on a flange – Natural gas metering station

- The ultrasound camera offers a sharp visualization of the leak. This image is straightforward to interpret, showing the leak location at a 90 cm distance. By approaching the leak, the operator can even see the exact position of the leak source.

- Seen by an OGI camera: a gas plume on the lower part of the flange, where a slightly higher contrast is observed. An expert operator with an experienced eye is needed in such cases to find the right angle to detect the leak and then to interpret the images1.
4. Methane leak on a flange bolt – Gas station
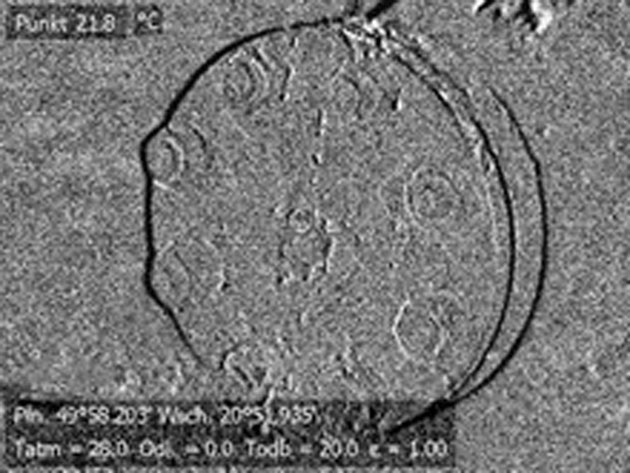


This leak could not be detected by the OGI camera due to windy conditions (~15 km/h), even using its high-contrast mode.
4. Methane leak on a flange bolt – Gas station


This leak could not be detected by the OGI camera due to windy conditions (~15 km/h), even using its high-contrast mode.
How do ALI and OGI techniques compare?
Acoustic Leak Imaging (ALI)
Optical Gas Imaging (OGI)
Detected gases
All gases, as long as the pressure difference is high enough (see below).
Also works for under-pressure (vacuum leaks).
Mainly hydrocarbons (although, with a different filter it’s possible to detect ammonia or CO2).
Not possible to detect IR-inactive molecules, such as hydrogen, nitrogen, air or noble gases.
Requirements for gas leak detection
Minimum pressure difference (50 mbar, 0.7 psi) at the leak site is required for a gas leak to emit ultrasounds.
A temperature difference between the cloud and the background is needed.
Factors affecting the detection capabilities
Ultrasound noises increase the detection limit of the camera.
However, Distran has strategies to improve gas leak detection in these cases.
Wind can dissipate the cloud making it hardly visible. Humidity, or the presence of residual gases absorbing in the specific infrared band negatively influence the detection.
Quantification
Real-time quantification by entering the type of gas and the system pressure in the camera’s interface.
Quantification requires using a tablet or a laptop, and a tripod to stabilize the image. It takes a few minutes to measure each leak. Estimations of leak rates are only available after a post-processing phase.
Calibration
Distran Ultra Pro: recommended only – every 4 years.
Recommended periodically (every 3-4 years) or even necessary according to each brand.
Operation in hazardous areas
Ultra Pro X was the first ultrasound camera on the market to receive the ATEX certification (intrinsically safe) in 2020.
It is now also certified under IECEx standards and holds UL certification for use in hazardous locations.
It also holds KCs certification (Korea).
Several OGI cameras come in intrinsically safe versions and hold similar certifications.
How do ALI and OGI techniques compare?
Detected gases
ALI: All gases, as long as the pressure difference is high enough (see below).
Also works for under-pressure (vacuum leaks).
OGI: Mainly hydrocarbons (although, with a different filter it’s possible to detect ammonia or CO2). Not possible to detect IR-inactive molecules, such as hydrogen, nitrogen, air or noble gases.
Requirements for gas leak detection
ALI: Minimum pressure difference (50 mbar, 0.7 psi) at the leak site is required for a gas leak to emit ultrasounds.
OGI: A temperature difference between the cloud and the background is needed.
Factors affecting the detection capabilities
ALI: Ultrasound noises increase the detection limit of the camera.
However, Distran has strategies to improve gas leak detection in these cases.
OGI: Wind can dissipate the cloud making it hardly visible. Humidity, or the presence of residual gases absorbing in the specific infrared band negatively influence the detection.
Quantification
ALI: Real-time quantification by entering the type of gas and the system pressure in the camera’s interface.
OGI: Quantification requires using a tablet or a laptop, and a tripod to stabilize the image. It takes a few minutes to measure each leak. Estimations of leak rates are only available after a post-processing phase.
Calibration
ALI: Distran Ultra Pro: recommended only – every 4 years.
OGI: Recommended periodically (every 3-4 years) or even necessary according to each brand.
Operation in hazardous areas
ALI: Ultra Pro X was the first ultrasound camera on the market to receive the ATEX certification (intrinsically safe) in 2020.
It is now also certified under IECEx standards and holds UL certification for use in hazardous locations.
It also holds KCs certification (Korea).
OGI: Several OGI cameras come in intrinsically safe versions and hold similar certifications.
Which method fits my application better?
Both ALI and OGI are advanced techniques for remote gas leak detection, improving inspection methods by easing and reducing time of inspection and by improving safety.
Optical Gas Imaging
disadvantages
Optical Gas Imaging
advantages
Along with the price, it reserves the tool for specialists. Extensive training and experience needed to operate and reliably find leaks.
Quantification of leak rates takes time and effort (tripod, post processing, …), and is not possible on all leaks.
Wind and humidity adversely affect the detection.
The only solution to detect at a distance hydrocarbon in vents, leaks on fuel tanks. No pressure difference between the container and the atmosphere is needed.
Compliant with OOOOa standards.
Acoustic Leak Imaging disadvantages
Acoustic Leak Imaging
advantages
Not suited for leak detection in systems with very low pressure differences.
Detection range is limited to 100 meters maximum.
The operator needs to learn to differentiate leaks from other ultrasound sources such as flow noise.
Only a 20-minute training is required for a basic use. Combined with a lower price than OGI devices, it can be made available to anyone, a particularly useful advantage in emergency cases.
Leak pictures are clearer, allowing a better documentation.
Leak rate quantification calculated and displayed live.
Detect leaks of any gas.
Which method fits my application better?
Both ALI and OGI are advanced techniques for remote gas leak detection, improving inspection methods by easing and reducing time of inspection and by improving safety.
Optical Gas Imaging disadvantages
Along with the price, it reserves the tool for specialists. Extensive training and experience needed to operate and reliably find leaks.
Quantification of leak rates takes time and effort (tripod, post processing, …), and is not possible on all leaks.
Wind and humidity adversely affect the detection.
Optical Gas Imaging advantages
The only solution to detect at a distance hydrocarbon in vents, leaks on fuel tanks. No pressure difference between the container and the atmosphere is needed.
Compliant with OOOOa standards.
Acoustic Leak Imaging disadvantages
Not suited for leak detection in systems with very low pressure differences.
Detection range is limited to 100 meters maximum.
The operator needs to learn to differentiate leaks from other ultrasound sources such as flow noise.
Acoustic Leak Imaging advantages
Only a 20-minute training is required for a basic use. Combined with a lower price than OGI devices, it can be made available to anyone, a particularly useful advantage in emergency cases.
Leak pictures are clearer, allowing a better documentation.
Leak rate quantification calculated and displayed live.
Detect leaks of any gas.
Which method fits my application better?
Both ALI and OGI are advanced techniques for remote gas leak detection, improving inspection methods by easing and reducing time of inspection and by improving safety.
Optical Gas Imaging disadvantages
Along with the price, it reserves the tool for specialists. Extensive training and experience needed to operate and reliably find leaks.
Quantification of leak rates takes time and effort (tripod, post processing, …), and is not possible on all leaks.
Wind and humidity adversely affect the detection.
Optical Gas Imaging advantages
The only solution to detect at a distance hydrocarbon in vents, leaks on fuel tanks. No pressure difference between the container and the atmosphere is needed.
Compliant with OOOOa standards.
Acoustic Leak Imaging disadvantages
Not suited for leak detection in systems with very low pressure differences.
Detection range is limited to 100 meters maximum.
The operator needs to learn to differentiate leaks from other ultrasound sources such as flow noise.
Acoustic Leak Imaging advantages
Only a 20-minute training is required for a basic use. Combined with a lower price than OGI devices, it can be made available to anyone, a particularly useful advantage in emergency cases.
Leak pictures are clearer, allowing a better documentation.
Leak rate quantification calculated and displayed live.
Detect leaks of any gas.
1 Detection Limits of Optical Gas Imaging for Natural Gas Leak Detection in Realistic Controlled Conditions
Daniel Zimmerle, Timothy Vaughn, Clay Bell, Kristine Bennett, Parik Deshmukh, and Eben Thoma
Environmental Science & Technology 2020 54 (18), 11506-11514
Read more on the topic:
Experience on using Acoustic Leak Imaging (ALI) Technology on Compressor Stations and Pressure Reducing Stations
Ana Gutiérrez-González and Florian Perrodin
Pipeline Technology Conference 2021, Berlin
White Paper Acoustic Leak Leak Imaging & Optical Gas Imaging comparison
Florian Perrodin
1 Detection Limits of Optical Gas Imaging for Natural Gas Leak Detection in Realistic Controlled Conditions
Daniel Zimmerle, Timothy Vaughn, Clay Bell, Kristine Bennett, Parik Deshmukh, and Eben Thoma
Environmental Science & Technology 2020 54 (18), 11506-11514
Read more on the topic:
Experience on using Acoustic Leak Imaging (ALI) Technology on Compressor Stations and Pressure Reducing Stations
Ana Gutiérrez-González and Florian Perrodin
Pipeline Technology Conference 2021, Berlin
White Paper Acoustic Leak Leak Imaging & Optical Gas Imaging comparison
Florian Perrodin
